Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder - A Comprehensive Guide
As the seasons change, so do our moods, energy levels, and overall well-being. While some people revel in the warmth of summer or the coziness of winter, others struggle with the transitions. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that affects millions worldwide, causing feelings of sadness, lethargy, and social withdrawal during specific times of the year.
What is Seasonal Affective Disorder?
SAD is a recognized mental health condition that occurs when the body's internal clock is disrupted by the changing seasons. The reduced sunlight during winter months or the increased heat during summer months can affect the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and melatonin, leading to feelings of depression and anxiety.
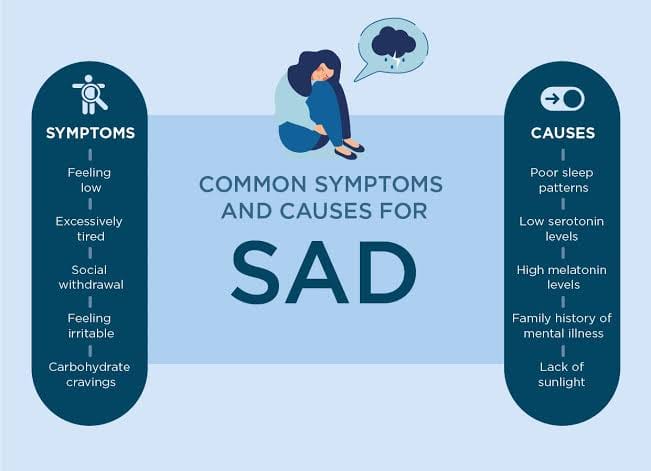
Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Feeling sad, empty, or hopeless most of the day
- Loss of energy and interest in activities
- Changes in appetite and sleep patterns
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
- Social withdrawal and avoidance of social situations
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact causes of SAD are still unknown, research suggests that it may be related to:
- Genetics: Family history plays a role in the development of SAD
- Geography: Living far from the equator increases the risk of SAD
- Age: Younger adults are more likely to experience SAD
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop SAD than men
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing SAD involves a comprehensive mental health evaluation, including:
- Physical exam
- Lab tests
- Psychological evaluation
Treatment options for SAD include:
- Light therapy: Exposure to bright artificial light
- Medications: Antidepressants and mood stabilizers
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, social support, and stress management
Coping with Seasonal Affective Disorder
While SAD can be challenging, there are ways to manage its symptoms:
- Stay active: Engage in regular physical activity
- Connect with others: Build a strong support network
- Practice self-care: Get enough sleep, eat a healthy diet, and relax
- Seek professional help: Consult a mental health professional
Conclusion: Finding Hope in the Seasons
Seasonal Affective Disorder may seem daunting, but with the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage its symptoms and find joy in every season. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we can work towards creating a more compassionate and supportive environment for those affected by SAD.













Comments ()