Uncovering the Hidden Dangers of Uterine Fibroids
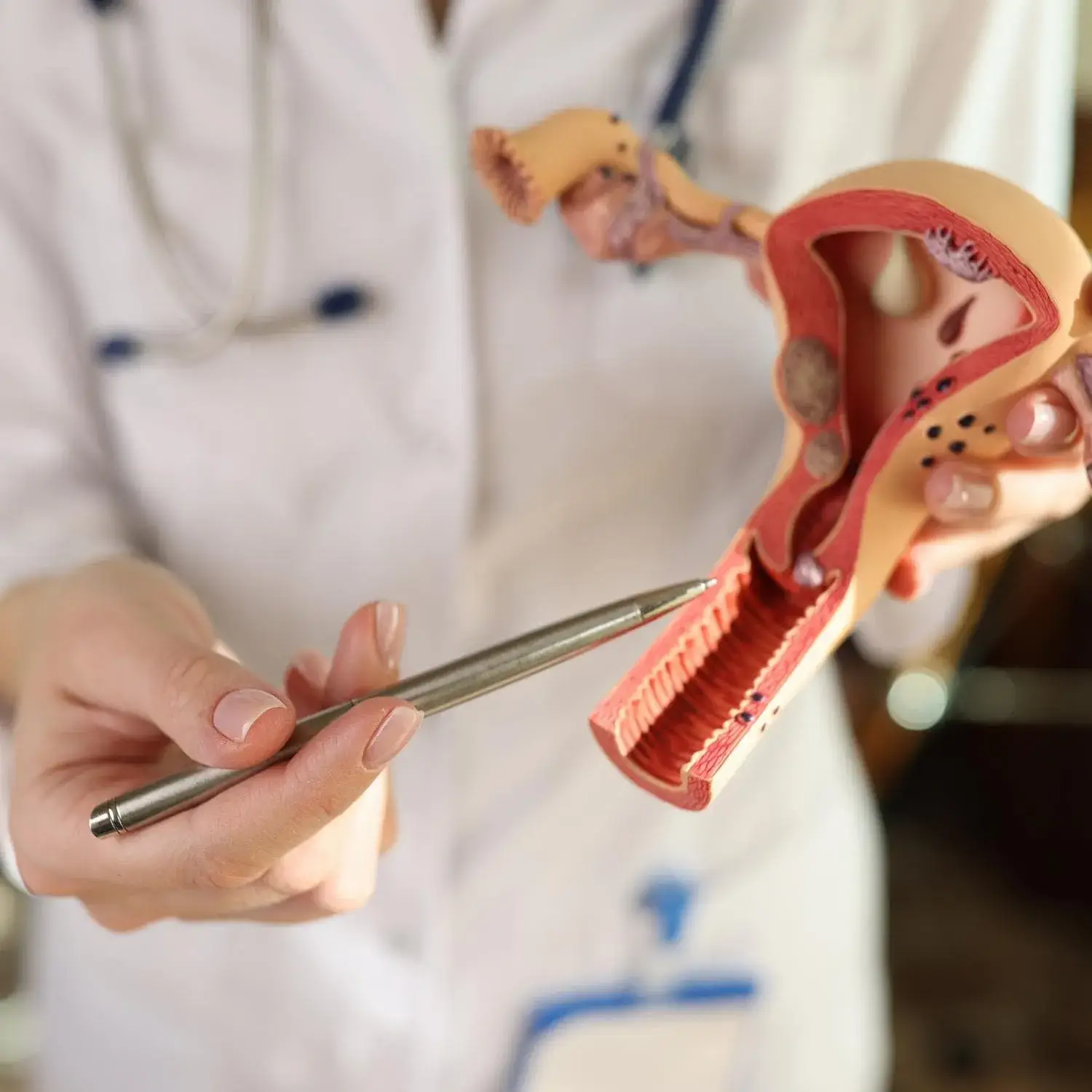
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are non-cancerous tumors that grow in the uterus. They are common, affecting more than 3 million women in the US each year.
Understanding Fibroids
Fibroids can vary in size, location, and number, and may cause symptoms such as:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Infertility
Fibroid Characteristics
Fibroids can be:
- Small or large, ranging from a pea to a grapefruit in size
- Located inside the uterine cavity, within the uterine wall, or on the outer surface of the uterus
- Single or multiple, with some women developing multiple fibroids
Impact on Women's Health
While fibroids are non-cancerous, they can significantly impact a woman's quality of life, causing:
- Discomfort and pain
- Heavy bleeding leading to anemia
- Fertility issues and pregnancy complications
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are classified into several types based on their location and growth pattern. Understanding these different types is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach.
1. Subserosal Fibroids
Subserosal fibroids grow under the lining of the outer surface of the uterus. They can put pressure on the surrounding organs, such as the bladder or bowel, leading to symptoms like pelvic pressure, frequent urination, or constipation.
2. Pedunculated Fibroids
Pedunculated fibroids attach to the uterus with a stalk or stem. They can grow either inside or outside the uterus and can cause symptoms like pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, or pressure on surrounding organs.
3. Intramural Fibroids
Intramural fibroids grow inside the muscle of the uterus. They are the most common type of fibroid and can cause symptoms like heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or pressure.
It's essential to note that some women may have multiple types of fibroids, and their location and size can impact the severity of symptoms. Accurate diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare provider are critical for managing uterine fibroids effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
Unraveling the Mystery of Uterine Fibroids
Despite extensive research, the exact cause of uterine fibroids remains unclear. However, several factors are believed to contribute to their development.
Genetic Mutations and Hormonal Imbalance
Gene changes and hormonal fluctuations are thought to play a significant role in the growth and development of uterine fibroids. These genetic mutations may affect the cells' ability to respond to hormones, leading to uncontrolled growth.
Identifying Risk Factors
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing uterine fibroids due to various risk factors, including:
- Being a person of reproductive age, as fibroids are most common during this stage
- Family history, as those with a first-degree relative (mother or sister) with fibroids are more likely to develop them
- Ethnicity, as African American women are more likely to develop fibroids than women of other ethnicities
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help women take proactive steps towards prevention and early detection.
Symptoms and Complications
Understanding the Hidden Dangers
While many individuals with uterine fibroids may not experience any noticeable symptoms, others may face a range of health issues that can significantly impact their quality of life. It's essential to be aware of these potential symptoms and complications to ensure timely medical attention.
Possible Symptoms
Some common symptoms associated with uterine fibroids include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding, leading to anemia and fatigue
- Pelvic pain, pressure, or discomfort
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
Potential Complications
If left untreated, uterine fibroids can lead to several complications, including:
- Anemia due to excessive menstrual bleeding
- Pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage, preterm labor, or fetal growth restriction
- Rare cases of cancer, such as leiomyosarcoma
It's crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you're experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about uterine fibroids. Early detection and treatment can help prevent these complications and improve overall health outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Uncovering the Hidden Dangers of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are often diagnosed during a routine pelvic exam or imaging tests. A healthcare provider may perform an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan to confirm the presence and size of fibroids. In some cases, a hysteroscopy or laparoscopy may be necessary to visualize the uterine cavity and surrounding organs.
Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids
Treatment options for uterine fibroids vary depending on the severity of symptoms, size, and location of fibroids, as well as the patient's reproductive goals. The following are some common treatment options:
Hormonal Drugs
Hormonal drugs, such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, may be prescribed to shrink fibroids and alleviate symptoms. These drugs work by reducing estrogen levels, which can help slow fibroid growth.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
An IUD, such as a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS), may be recommended to reduce heavy bleeding and cramping associated with fibroids.
Surgical Intervention
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove fibroids or the uterus. Common surgical procedures include:
- Myomectomy: removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus
- Hysterectomy: removal of the uterus
- Endometrial ablation: removal of the uterine lining
It's essential to discuss the risks and benefits of each treatment option with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for individual cases.












Comments ()