Revolutionizing Protein Production - The Rise of Cultured Meat
The Need for Alternative Protein Sources
The world is on the cusp of a protein revolution, and it's essential to understand the driving forces behind this shift. The global population is growing at an unprecedented rate, projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050. This growth puts immense pressure on traditional animal agriculture, which faces significant sustainability challenges.
Sustainability Challenges in Traditional Animal Agriculture
Animal agriculture is a leading cause of greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. The industry's environmental footprint is substantial, accounting for:
- 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions
- 70% of global freshwater usage
- 30% of global land usage
The Promise of Cultured Meat
Cultured meat, also known as clean meat or in-vitro meat, offers a promising solution to these challenges. By producing meat in a controlled environment, we can:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 96%
- Minimize water usage by up to 99%
- Eliminate the need for animal slaughter and reduce animal welfare concerns
Cultured meat provides a stable protein supply without compromising on taste, texture, or nutritional value. This innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume protein, ensuring a sustainable food future for generations to come.
Understanding Cultured Meat Production
Cultured meat, also known as clean meat or in vitro meat, is a revolutionary approach to producing meat that doesn't involve raising and slaughtering animals. This innovative method uses cell culture technology to produce meat outside of animals, reducing the environmental impact and ethical concerns associated with traditional animal farming.
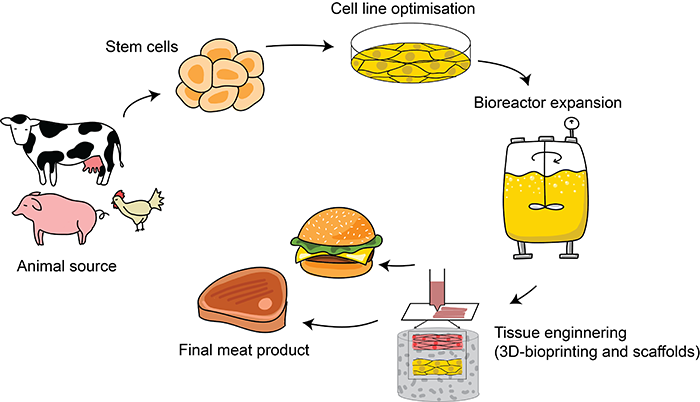
How Cultured Meat Production Works
Animal cells are taken from a donor animal through a biopsy or from cell banks. These cells are then grown in a controlled environment, called a bioreactor, where they are nourished with a nutrient-rich medium. The cells multiply and form muscle tissue, which is then harvested and processed into cultured meat.
Benefits of Cultured Meat Production
By eliminating the need for animal farming, cultured meat production offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution
- Improved animal welfare and reduced risk of animal-borne diseases
- Increased food safety and reduced risk of antibiotic resistance
- Customizable nutritional content and taste
Challenges and Future Directions
While cultured meat production holds great promise, there are still challenges to overcome, such as:
- Scalability and cost-effectiveness
- Regulatory frameworks and public acceptance
- Continued research and development to improve taste, texture, and nutritional content
As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see cultured meat become a more viable and sustainable option for meat production.
Benefits of Cultured Meat
Cultured meat, also known as clean or in-vitro meat, is poised to revolutionize the way we produce protein. This groundbreaking technology offers numerous benefits that address some of the most pressing concerns associated with traditional animal agriculture.
Environmental Sustainability
One of the most significant advantages of cultured meat is its reduced environmental impact. Traditional animal agriculture accounts for approximately 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with the livestock industry requiring vast amounts of land, water, and feed. In contrast, cultured meat production requires:
- Up to 96% less land
- Up to 96% less water
- Up to 70% less feed
By minimizing these resources, cultured meat helps mitigate deforestation, habitat destruction, and water pollution, making it a more sustainable option for meeting the world's growing protein demands.
Improved Animal Welfare
Cultured meat eliminates the need for animal slaughter and breeding, significantly improving animal welfare. Traditional animal agriculture raises concerns about:
- Inhumane living conditions
- Painful procedures
By bypassing animal exploitation, cultured meat promotes a more compassionate food system.
Enhanced Nutrition and Food Safety
Cultured meat offers the potential for tailored nutritional profiles and reduced foodborne illnesses. Scientists can:
- Optimize fatty acid composition
- Enhance vitamin and mineral content
- Reduce saturated fat and cholesterol levels
- Minimize the risk of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Additionally, cultured meat reduces the risk of foodborne pathogens, such as Salmonella and E. coli, commonly associated with traditional meat production.
As the world's population continues to grow, cultured meat presents a viable solution for sustainable, humane, and healthier protein production. With its numerous benefits, cultured meat is poised to revolutionize the way we produce and consume meat.
Challenges and Considerations
Technical Challenges in Scaling Up Production and Reducing Costs
The cultured meat industry faces significant technical challenges in scaling up production and reducing costs. Currently, the process of producing cultured meat is labor-intensive and expensive, making it challenging to compete with traditional meat production methods. To address this, companies are investing in automation and process optimization to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Regulatory Frameworks and Public Acceptance Need to be Addressed
Another significant challenge is the need for clear regulatory frameworks and public acceptance. Governments and regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to classify and regulate cultured meat products. Moreover, public acceptance and education are crucial for the adoption of cultured meat. Companies must invest in marketing and educational campaigns to raise awareness and build trust with consumers.
Ensuring the Quality and Safety of Cultured Meat Products
Ensuring the quality and safety of cultured meat products is paramount. Companies must implement rigorous quality control measures to guarantee the consistency and safety of their products. This includes developing robust testing protocols and ensuring compliance with food safety regulations. Additionally, transparency and traceability throughout the production process are essential for building consumer trust.
The Future of Food: Cultured Meat's Potential
Cultured meat, a revolutionary innovation in the food industry, has the potential to transform the way we produce and consume meat. This cutting-edge technology involves growing animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need for animal slaughter and reducing the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming.
Transforming the Food Industry
Cultured meat could revolutionize the food industry by offering a sustainable alternative to traditional meat. With the global demand for meat projected to increase by 70% by 2050, cultured meat provides a viable solution to meet this demand without compromising on taste, quality, or food safety.
Overcoming Challenges
Ongoing research and development aim to overcome the challenges associated with cultured meat production, such as high production costs, limited scalability, and regulatory frameworks. Scientists and companies are working together to improve cell lines, culture media, and bioreactor designs to make cultured meat more efficient and cost-effective.
Bringing Cultured Meat to Market
As cultured meat advances towards commercialization, companies are working to bring products to market. With several products already available in select markets, the future of food looks promising. Cultured meat has the potential to not only transform the food industry but also contribute to a more sustainable and food-secure future.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dog-treats-glass-storage-container-3f5d7e36-81df4011d844459c9272c9c8404bc38d.jpg)











Comments ()