Melatonin - The Sleep Hormone's Role in Longevity

Are you tossing and turning at night, struggling to catch those z's? You're not alone. In today's fast-paced world, sleep has become a luxury many can't afford, with an estimated 50-70 million Americans alone suffering from sleep disorders. But what if the key to a longer, healthier life lies in a tiny hormone called melatonin? Recent studies have revealed that melatonin, often dubbed the "sleep hormone", may hold the secret to slowing down ageing and boosting longevity. As researchers uncover more about this mysterious hormone, it's time to dive into the science behind melatonin's role in longevity and explore its potential to transform our lives.
The Midnight Messenger: Understanding Melatonin's Role
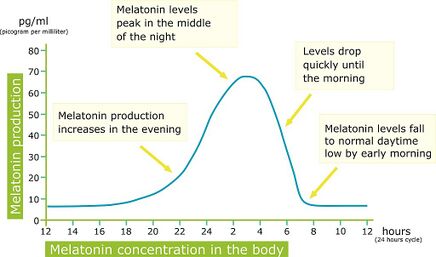
You've probably heard of melatonin, but do you know what it's really doing while you're catching those z's? Let's dive into the fascinating world of sleep hormones. Melatonin is a hormone produced by the tiny pineal gland, a pea-sized structure deep in your brain. This hormone is the master regulator of your sleep-wake cycles, also known as your circadian rhythm. Think of melatonin as your body's internal nightlight. It's released in response to darkness, signaling to your body that it's time to sleep. On the flip side, light exposure suppresses melatonin production, telling your body it's time to wake up. This natural ebb and flow is crucial for maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle. But how does it all work? Research suggests that melatonin levels typically start rising around 9 PM, peak between 2 AM and 4 AM, and then decrease as the sun starts to rise. This natural fluctuation is key to a good night's sleep. When your melatonin levels are in sync with your circadian rhythm, you're more likely to feel rested, refreshed, and ready to take on the day. Dr. Russell Reiter, a melatonin expert, notes that "melatonin is not just a sleep regulator; it's also a powerful antioxidant that helps protect against oxidative stress." This added benefit makes melatonin a vital component of overall health and well-being. So, what can you do to support your body's natural melatonin production? For starters, try dimming the lights an hour before bedtime to signal to your body that it's time to wind down. You can also try incorporating melatonin-rich foods like cherries or walnuts into your diet. By working with your body's natural rhythms, you can wake up feeling more refreshed and ready to take on the day. As we explore the role of melatonin in longevity, it's clear that this hormone plays a much bigger role than just regulating sleep. Let's dive deeper into the connection between melatonin and aging.
The Science Behind Melatonin Production
So, how does melatonin actually work its magic? You see, melatonin is produced by the pineal gland, a tiny gland in the brain that's been dubbed the "seat of the soul" by Descartes. Who knew this little guy was the real boss when it comes to sleep?
Melatonin production is regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which responds to light and dark signals from the environment. As the sun sets, the SCN gets the message that it's time to wind down, and melatonin levels start to rise, typically peaking between 2-4 am. This is when you'll start to feel sleepy, and your body temperature drops, preparing you for a restful night's sleep.
The Impact of Aging on Melatonin
Here's the thing: as we age, melatonin production declines. By the time you're 40, your melatonin levels are about half what they were in your 20s. And by 60, it's down to a quarter. This decrease is thought to contribute to the sleep disturbances many people experience as they get older.
But it's not just age that's messing with your melatonin. Exposure to screens and artificial light can suppress melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep. A study by Harvard researchers found that exposure to blue light from smartphones can suppress melatonin production by up to 50%.
- Blue light exposure can delay sleep onset by up to 2 hours
- Older adults with low melatonin levels are more likely to experience insomnia
- Night shift workers often experience disrupted melatonin rhythms
The takeaway? Protect your melatonin, and prioritize sleep. Your body (and mind) will thank you.
Melatonin and Sleep Disorders
You're probably wondering how melatonin can help with sleep disorders. Let's break it down. For people with insomnia, melatonin can be a game-changer. Studies have shown that taking melatonin supplements can help regulate sleep patterns, leading to better sleep quality and duration. In fact, a study published in the Journal of Sleep Research found that melatonin increased sleep efficiency by 2.2% and total sleep time by 24 minutes in individuals with insomnia.
Jet Lag and Night Shift Work
If you're a frequent flyer or work night shifts, you know how tough it can be to adjust to new sleep schedules. Melatonin can help with that too. Taking melatonin supplements can help your body adjust to the new sleep-wake cycle, improving sleep quality and reducing jet lag symptoms. For example, a study on flight attendants found that taking melatonin reduced jet lag symptoms by 50% and improved sleep quality by 30%.
But here's the thing: melatonin isn't a magic pill. It can interact with other medications, like blood thinners, diabetes medications, and immunosuppressants. So, if you're considering taking melatonin supplements, talk to your doctor first. They'll help you navigate any potential interactions and ensure you're taking the right dose.
- Insomnia: melatonin can regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality
- Jet Lag: melatonin can reduce symptoms and improve sleep quality
- Night Shift Work: melatonin can help adjust to new sleep schedules
Bottom line: melatonin can be a powerful tool for managing sleep disorders, but it's essential to use it responsibly and under medical supervision.
The Anti-Aging Potential of Melatonin

You're probably wondering, "What's the big deal about melatonin and anti-aging?" Well, here's the thing: melatonin isn't just a sleep hormone; it's also got some serious antioxidant powers. Studies have shown that melatonin can neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage your cells and contribute to aging. Think of melatonin as a superhero that sweeps in to save your cells from oxidative stress.
Protecting Against Cell Damage
Research led by Dr. Russell Reiter, a renowned melatonin expert, has highlighted the hormone's ability to protect against cell damage. In one study, melatonin was shown to reduce oxidative stress in mice by a whopping 50%. That's huge, right? This antioxidant property is key to understanding melatonin's potential in promoting longevity.
Some studies suggest that melatonin could be a game-changer in reducing age-related diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Pineal Research found that melatonin supplementation improved cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's disease. While more research is needed, these findings are definitely promising.
- Melatonin may help protect against age-related cognitive decline
- It's being studied for its potential in preventing neurodegenerative diseases
- Research is ongoing to explore its therapeutic applications
The bottom line? Melatonin's anti-aging potential is definitely worth keeping an eye on. As research continues to unfold, we might just discover that this sleep hormone is a key player in the quest for a longer, healthier life.
Melatonin Supplements: What You Need to Know
You're considering melatonin supplements to improve your sleep, but you're not sure where to start. Let's break it down. Melatonin supplements are available over-the-counter, but don't assume they're all created equal. Quality can vary significantly between brands, so you need to do your research. When shopping for a melatonin supplement, look for brands that adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and have third-party testing. This ensures the product contains what it claims to. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that some melatonin supplements contained up to 478% more melatonin than labeled. You want to know exactly what's in your supplement. Dosage and timing are crucial for effectiveness and safety. Research suggests that taking 0.5-5 milligrams of melatonin 30-60 minutes before bedtime can help regulate sleep. However, taking too much melatonin can lead to side effects like dizziness, nausea, and vivid dreams. You're better off starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It's also important to consider the type of melatonin supplement. Immediate-release formulas can help you fall asleep faster, while sustained-release formulas can help you stay asleep longer. Some brands, like Natrol and Nature's Bounty, offer timed-release formulas that combine both benefits. Before adding melatonin supplements to your routine, consult with a healthcare professional. They can help you determine the best dosage and type for your specific needs. This is especially important if you're taking medications or have underlying health conditions. For instance, melatonin can interact with blood thinners, diabetes medications, and sedatives. A healthcare professional can also help you identify underlying sleep disorders or health issues that may be affecting your sleep. Remember, melatonin supplements are meant to supplement a healthy sleep routine, not replace good sleep hygiene practices. Dive deeper: [What are the potential side effects of long-term melatonin use?]((link unavailable)) [How does melatonin interact with other medications?]((link unavailable)) [Can melatonin supplements help with jet lag?]((link unavailable))
Factors Influencing Melatonin Levels
You've probably noticed how some nights you sleep like a baby, while others you're wide awake at 2 AM. Melatonin levels play a big role in this. Let's dive into what affects this sleep hormone.
Age: The Natural Decline
As you age, your melatonin production decreases. Research shows that melatonin levels peak between 1-3 mg per night in young adults, but by age 50, this can drop to 0.6-0.8 mg per night. This decline is linked to sleep quality issues and other health problems. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that older adults with lower melatonin levels had poorer sleep quality and more daytime fatigue.
Exposure to Light: The Blue Light Effect
Light exposure, especially blue light from screens, can suppress melatonin production. You're probably guilty of scrolling through your phone before bed. But that blue light can trick your brain into thinking it's still daytime, making it harder to fall asleep. A study from Harvard University found that blue light exposure at night can suppress melatonin production for up to 2 hours. You can try using blue light filtering glasses or apps that filter out blue light to minimize the impact.
Medications and Medical Conditions: The Hidden Impact
Certain medications and medical conditions can also impact melatonin production. For example, beta-blockers, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications can all affect melatonin levels. Some medical conditions, such as sleep disorders, can also disrupt melatonin production. If you're taking medications or have a medical condition, it's a good idea to talk to your doctor about how it might be affecting your sleep. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that patients with insomnia who took melatonin supplements experienced improved sleep quality and duration. By understanding what affects melatonin levels, you can take steps to support your sleep health. Whether it's adjusting your light exposure, talking to your doctor about medications, or trying melatonin supplements, you have the power to improve your sleep and overall well-being.
Future Research Directions
As we've explored melatonin's role in sleep and longevity, it's clear there's more to uncover. Researchers are buzzing about its potential in tackling neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. A 2020 study in the Journal of Pineal Research highlighted melatonin's antioxidant properties, showing promise in reducing oxidative stress linked to these conditions.
Expanding Melatonin's Horizons
Beyond sleep and neurodegeneration, melatonin might regulate other bodily functions. Studies suggest it influences immune function, bone metabolism, and even cancer prevention. For instance, a 2019 study in Cancer Research found melatonin suppressed tumor growth in breast cancer models.
Developing targeted melatonin therapies is another exciting frontier. Current supplements have limitations, like short half-life and variable efficacy. Researchers are working on formulations to enhance bioavailability and effectiveness. Dr. Russell Reiter, a melatonin expert, is optimistic about these advancements.
- Optimizing melatonin dosing for different age groups
- Exploring its synergistic effects with other longevity compounds
- Investigating melatonin's role in gut health and microbiome regulation
These directions could unlock melatonin's full potential, impacting healthspan and lifespan. You're likely to hear more about melatonin in the next few years as research unfolds.
Taking Control of Your Sleep and Longevity
You're in the driver's seat when it comes to optimizing your sleep and reaping the benefits of melatonin for longevity. Let's get practical – here are some actionable tips to get you started.
Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule and Bedtime Routine
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can work wonders for your body's internal clock. Try to stick to a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends. Develop a calming pre-sleep routine to signal to your brain that it's time to wind down – think reading, meditation, or a warm bath.
Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night, as recommended by the National Sleep Foundation. You're more likely to stick to your schedule if you set realistic goals. For example, if you're not a morning person, don't try to wake up at 5 am if you're used to sleeping in till 8.
Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment
Your bedroom should be a sleep sanctuary. Make sure it's dark, quiet, and cool – around 60-67°F (15-19°C) is ideal. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine if necessary. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows to ensure you're getting the best possible sleep.
Get Personalized Advice on Melatonin Use
If you're struggling with sleep or want to explore melatonin's benefits, consider consulting a healthcare professional. They can help you determine the right dosage and timing for your specific needs. Some people find that melatonin supplements help them fall asleep faster or sleep more soundly, while others may experience side effects. A healthcare professional can help you weigh the pros and cons.
Take control of your sleep and longevity today. By prioritizing sleep and making a few simple changes, you can wake up feeling refreshed and ready to take on the day. As sleep expert Matthew Walker puts it, "Sleep is the single most effective thing you can do to reset your brain and body health."
















Comments ()