Lab-Grown Meat Production Process
Imagine a world where your burger doesn't contribute to deforestation, animal suffering, or antibiotic resistance. Welcome to the future of food, where lab-grown meat is revolutionizing the way we think about protein. With over 150 companies worldwide investing in this technology, including major players in the US, Singapore, and Europe, lab-grown meat is poised to disrupt the $1.5 trillion meat industry. In fact, Singapore became the first country to approve lab-grown chicken in 2020, and the US followed suit in 2022, with the FDA approving two companies to sell cell-cultivated chicken. But how does it work? Let's dive into the fascinating process of lab-grown meat production.
The Future of Food: Lab-Grown Meat Takes Center Stage
Lab-grown meat, also known as clean meat, is produced by growing animal cells in a controlled environment. Imagine a world where burgers, steaks, and chicken nuggets are created without the need for animal slaughter. Sounds like science fiction, right? Well, it's not. Companies like Memphis Meats and Mosa Meat are investing heavily in this innovative approach, anticipating a shift in consumer preferences. In fact, Memphis Meats has already raised over $180 million in funding to develop its lab-grown meat products. You're probably wondering how this works. It's quite simple, really. Scientists take animal cells and grow them in a nutrient-rich environment, allowing them to multiply and form into the desired shape. This approach not only reduces animal slaughter but also minimizes the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming. According to a study by the University of Oxford, lab-grown meat could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 96% compared to traditional beef production. The numbers are promising, and experts are taking notice. "Lab-grown meat has the potential to disrupt the entire meat industry," says Kate Krueger, director of science and technology at the Good Food Institute. With companies like Tyson Foods and Cargill investing in lab-grown meat, it's clear that this technology is here to stay. In fact, the global lab-grown meat market is expected to reach $140 million by 2023, up from just $15 million in 2019. So, what does this mean for you? For starters, you might be seeing lab-grown meat products on your grocery store shelves soon. Companies are working to make these products affordable and accessible to consumers. And let's be real – who wouldn't want to indulge in a juicy burger that's not only delicious but also sustainable? As the demand for environmentally friendly and cruelty-free products continues to rise, lab-grown meat is poised to become a major player in the food industry.
Cell Collection and Isolation
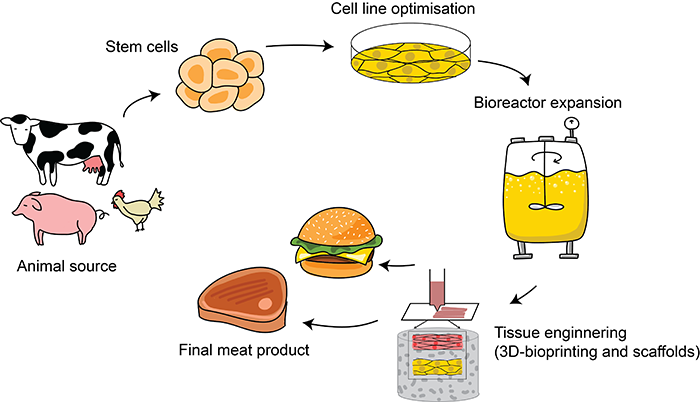
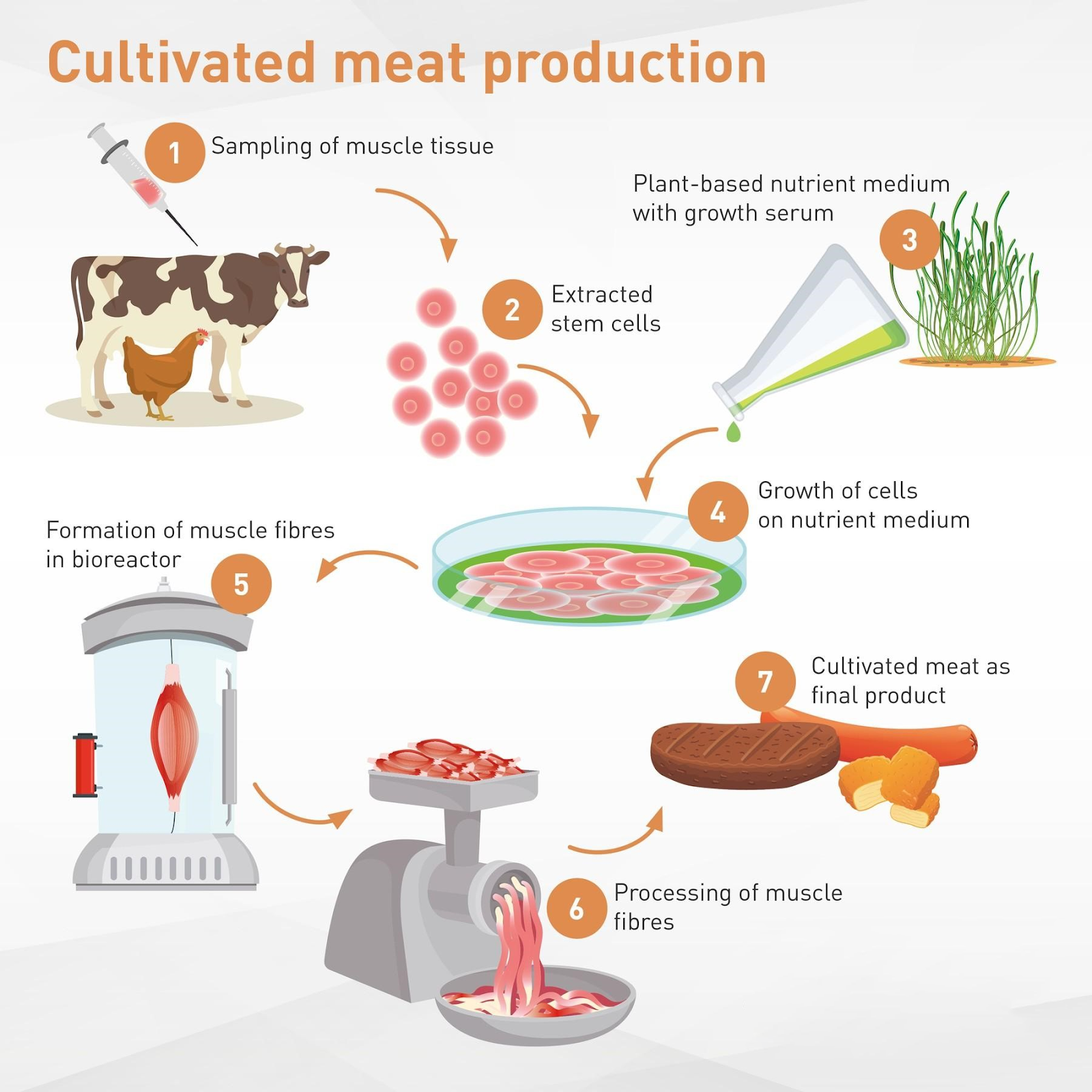
So, you've learned about the basics of lab-grown meat. Now, let's dive into the nitty-gritty of how it's made, starting with cell collection and isolation. Cells are typically collected from animals through a biopsy or other non-invasive methods. For example, companies like Memphis Meats and Mosa Meat have successfully collected cells from cows, chickens, and even fish without harming the animals.
The Isolation Process
The collected cells are then isolated and prepared for cultivation. This involves separating the cells from the tissue and breaking them down into individual cells. It's a bit like taking a puzzle apart, piece by piece, to get the individual components. Researchers use enzymes to break down the tissue, and then they isolate the specific cell types they need.
You're probably wondering what kind of cells are used. Well, muscle cells, fat cells, and other cell types are used to create a diverse range of products. For instance, muscle cells are used to create the tender, juicy texture of meat, while fat cells add flavor and marbling. Companies like JUST and Aleph Farms are experimenting with different cell combinations to create the perfect blend.
- Muscle cells (myocytes) for texture and structure
- Fat cells (adipocytes) for flavor and marbling
- Connective tissue cells (fibroblasts) for support and texture
The isolated cells are then used to create cell lines, which are essentially a batch of cells that can be grown and expanded in the lab. This is where the magic happens, and the cells start to multiply and grow into the meat products we know and love.
Cell Culture and Proliferation
You're getting into the meat of the process – pun intended! Cell culture is where the magic happens, and your lab-grown meat starts to take shape. So, let's dive into the specifics. Cells are cultured in a nutrient-rich medium, allowing them to grow and multiply. This medium is carefully formulated to provide the perfect blend of nutrients, growth factors, and other essential components. For example, companies like Memphis Meats use a medium that's rich in proteins, sugars, and other nutrients that support cell growth.
Controlling the Environment
The culture medium is carefully controlled to promote cell growth and differentiation. You're talking precision temperature control, pH levels, and oxygen levels – all crucial for optimal cell growth. Some companies use bioreactors, like the ones developed by biotech firm, ABEC, which provide a controlled environment for cells to thrive.
Let's talk numbers. Did you know that cell cultures can achieve densities of up to 10 million cells per milliliter? That's a lot of cells! And to achieve this, companies like Just are working on optimizing their cell culture protocols to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Quality Control
Cells are monitored for contamination and other quality control measures. You can't afford to have any unwanted bacteria or other contaminants sneaking into your cell culture – that would be a disaster! To prevent this, companies use strict quality control measures, like regular testing and monitoring of cell cultures. For instance, Aleph Farms, a leading player in the lab-grown meat industry, uses advanced microscopy and microbiological testing to ensure their cell cultures are contaminant-free.
- Regular testing for contaminants like bacteria, yeast, and mold
- Monitoring cell growth and proliferation rates
- Maintaining optimal culture conditions
By controlling the environment and monitoring cell health, you're able to produce high-quality cells that are ready for the next step in the process. And that's where the excitement really starts to build – you're one step closer to sinking your teeth into a juicy lab-grown burger!
Scaffold Development and Cell Attachment

So, you've learned how the cell harvesting process works. Now, let's dive into the next crucial step: scaffold development and cell attachment. This is where things get really interesting - a scaffold is created to provide structure and support for cell growth, kind of like a 3D printing framework for your meat.
The scaffold is designed to mimic the natural environment of animal tissue, providing the right conditions for cells to attach and grow. Companies like Aleph Farms and Memphis Meats are using innovative materials like collagen and plant-based scaffolds to create the perfect environment for cell growth. These scaffolds are engineered to have the right texture, porosity, and biochemical signals to support cell attachment and proliferation.
How it Works
Cells attach to the scaffold, forming a tissue-like structure. This is a critical step, as it allows the cells to organize and interact with each other, just like they would in an animal's body. The scaffold provides a surface for the cells to adhere to, and it's usually coated with proteins and growth factors that help stimulate cell growth and differentiation.
- The scaffold's surface topography is designed to mimic the extracellular matrix of animal tissue
- Cells attach to the scaffold through specific adhesion molecules, like integrins
- The scaffold's mechanical properties are tailored to match the native tissue environment
For example, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have developed a scaffold made from decellularized plant material that's been shown to support the growth of muscle cells and even induce the formation of blood vessels. It's a game-changer for lab-grown meat production!
Tissue Maturation and Harvesting
So, you've got your cell culture thriving, and it's time to take it to the next level. This is where tissue maturation comes in – it's like the meat is going to the gym to bulk up and develop that perfect texture and flavor. Companies like Memphis Meats are working on perfecting this process, and it's fascinating stuff. They're using bioreactors to mimic the conditions that muscle tissue would experience in an animal, like stretching and contracting, to get that realistic texture.
The Waiting Game
The tissue is matured for around 2-3 weeks, depending on the type of meat being produced. During this time, the cells are constantly monitored and nurtured to ensure they're developing just right. It's a bit like baking a cake – you can't rush perfection. For instance, when making lab-grown chicken, scientists might focus on getting that tender breast meat just right, while for lab-grown beef, they're going for that perfect marbling.
Once the tissue has reached the desired level of maturity, it's time for harvesting. This is a delicate process, as you don't want to damage the tissue and compromise the quality of the meat. The lab-grown meat is carefully harvested and prepared for processing. Companies like JUST are exploring different harvesting methods, including using enzymes to gently break down the tissue.
- Quality control checks are carried out to ensure the product meets safety standards
- The meat is tested for contaminants and pathogens
- Nutritional content is analyzed to ensure it meets regulatory requirements
After passing quality control, the lab-grown meat is ready to be packaged and shipped out to restaurants and stores. It's a complex process, but the end result is a product that's not only cruelty-free but also potentially more sustainable and healthier than traditional meat.
Scaling Up Production
You're probably wondering how lab-grown meat companies plan to meet the growing demand for this innovative product. Companies like Memphis Meats and Just are working tirelessly to scale up production, and it's exciting to see the progress they're making. For instance, Memphis Meats is building a 4,000-square-foot production facility in California that's expected to produce over 40,000 pounds of lab-grown meat per year.
The Challenges of Scaling Up
Scaling up production isn't without its challenges, though. One of the main hurdles is reducing costs. Currently, lab-grown meat is still relatively expensive to produce, making it difficult to compete with traditional meat prices. However, advances in technology and process optimization are helping to drive down costs. For example, companies are developing more efficient bioreactors that can produce more meat in less time, which in turn reduces energy and nutrient costs.
Another key area of focus is optimizing the cell culture process. By fine-tuning the nutrient-rich broth and growth factors, companies can increase cell yield and reduce waste. This not only reduces costs but also improves the overall sustainability of the process. According to a study by the Good Food Institute, lab-grown meat has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 96% compared to traditional meat production.
- Advances in bioreactor design are increasing production efficiency
- Companies are exploring new cell lines and growth factors to improve yield
- Collaborations with food companies and research institutions are driving innovation
As production costs continue to decrease, lab-grown meat is poised to become a significant player in the global meat market. With companies like Beyond Meat and Tyson Foods investing heavily in lab-grown meat, it's clear that this technology is here to stay. So, are you ready to take a bite out of the future of meat?
What's Next for Lab-Grown Meat?
You're probably wondering what's next for lab-grown meat. Regulatory approval is a major hurdle, but companies like Memphis Meats and Just are already making progress. They're working closely with regulatory bodies like the US FDA to ensure their products meet safety standards.
The Road to Market Success
But here's the thing: regulatory approval is just the first step. Consumer acceptance and education are crucial for lab-grown meat to become a mainstream option. According to a survey by the Good Food Institute, 60% of consumers are open to trying lab-grown meat. That's a promising start, but there's still work to be done to build trust and awareness.
Ongoing innovation will be key to driving growth and expansion in the lab-grown meat industry. We're already seeing advancements in cell culture media, scaffold technology, and bioreactor design. These innovations will help reduce production costs, improve product texture, and increase scalability.
- Companies are exploring new applications, such as seafood and foie gras
- Partnerships with traditional meat companies could accelerate market penetration
- Investors are pouring millions into lab-grown meat startups
The future of lab-grown meat looks bright, and you can be a part of it. As a consumer, staying informed and open-minded will help shape the industry's trajectory. Who knows – your next burger might just be lab-grown!


















Comments ()