Decoding Intel's CPU Hierarchy - What Makes an i3, i5, or i7?
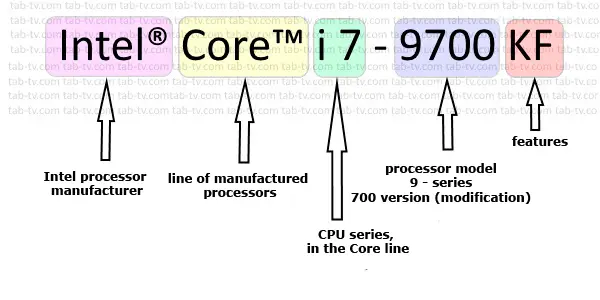
Navigating the world of computer hardware can feel like learning a new language, especially when faced with a sea of seemingly cryptic terms like "i3," "i5," and "i7." These designations represent Intel's core processor lineup, and understanding their differences is crucial for selecting a computer that meets your performance needs. While the naming convention might initially seem arbitrary, it actually provides key insights into the capabilities of each processor class.
Beyond the Numbers: Key Differentiators
While the "i" prefix remains consistent, the succeeding number – 3, 5, or 7 – signifies a different tier of processing power. Here's a breakdown of the key factors that separate these CPU classes:
1. Core Count and Threads: The Engine Room
At the heart of every CPU lie its cores – processing units that handle instructions and calculations. Generally:
- **i3:** Entry-level processors typically featuring 2 cores with hyperthreading, allowing them to process 4 threads simultaneously.
- **i5:** Mid-range processors usually offering 4 or 6 cores, with hyperthreading often present in the 4-core variants. This translates to 8 threads for 4-core models and 6 or 12 threads for the 6-core versions.
- **i7:** High-performance processors starting with 6 cores and often reaching 8 or more, most with hyperthreading. This results in 12 or more threads for efficient multitasking.
More cores and threads translate to smoother performance, especially when handling multiple applications simultaneously or demanding software like video editing programs.
2. Clock Speed: The Tempo of Processing
Measured in gigahertz (GHz), clock speed refers to the rate at which a CPU executes instructions. Higher clock speeds generally equate to faster performance, particularly for single-threaded tasks:
- **i3:** Typically have base clock speeds in the 2-3 GHz range, suitable for basic tasks and light multitasking.
- **i5:** Generally operate at higher base clock speeds, often between 3-4 GHz, enabling smoother performance for demanding applications and gaming.
- **i7:** Offer the highest base clock speeds, frequently exceeding 4 GHz, delivering exceptional responsiveness for intensive workloads and high-refresh-rate gaming.
However, clock speed isn't the sole determinant of performance. The architecture, core count, and cache size also play significant roles.
3. Cache Memory: The Information Expressway
Cache acts as a high-speed memory buffer between the CPU and the main RAM. It stores frequently accessed data, allowing the CPU to retrieve information quickly. Larger cache sizes can lead to faster program loading and smoother multitasking:
- **i3:** Generally have smaller cache sizes, ranging from 4MB to 8MB, which is sufficient for basic computing tasks.
- **i5:** Typically offer larger cache sizes compared to i3, usually between 6MB and 12MB, contributing to their improved performance in multitasking and demanding applications.
- **i7:** Boast the largest cache sizes, often starting at 8MB and going up to 16MB or more, allowing for lightning-fast data access and exceptional multitasking capabilities.
Generational Shifts: Beyond the i-Series Labels
Adding another layer of complexity, Intel releases new processor generations annually, denoted by a generation number following the i-series designation. For example, an 11th Gen Intel Core i5 processor would be identified as an "i5-11xxx," while a 13th Gen Intel Core i7 processor might be labeled "i7-13xxx."
Each new generation typically introduces architectural improvements, potentially leading to:
- Increased core counts within each i-series tier.
- Higher clock speeds for improved performance.
- Larger cache sizes for faster data access.
- Support for newer technologies and standards, such as faster RAM or Wi-Fi.
Choosing the Right "i" for You
Ultimately, the "best" i-series processor depends on your specific needs and budget:
- **i3:** Ideal for everyday tasks like browsing, email, and light productivity work. Cost-effective for budget-conscious users.
- **i5:** Strikes a balance between performance and affordability, suitable for moderate multitasking, gaming, and content creation.
- **i7:** Offers the highest performance for demanding workloads, including video editing, 3D rendering, and high-end gaming.
In Conclusion: Navigating the Processor Landscape with Confidence
Understanding the distinctions between Intel's i3, i5, and i7 processors empowers you to make informed decisions when choosing a computer. By considering your computing needs, budget, and the factors outlined above – core count, clock speed, cache size, and generation – you can confidently select the processor that aligns with your digital lifestyle. Remember to delve into the specifics of each processor model, as variations exist even within the i-series tiers. Armed with this knowledge, you can navigate the world of computer hardware with clarity and find the perfect processor to fuel your digital endeavors.











Comments ()