Cultivated Meat's Next Hurdle - Scaling Up Production for Mass Consumption
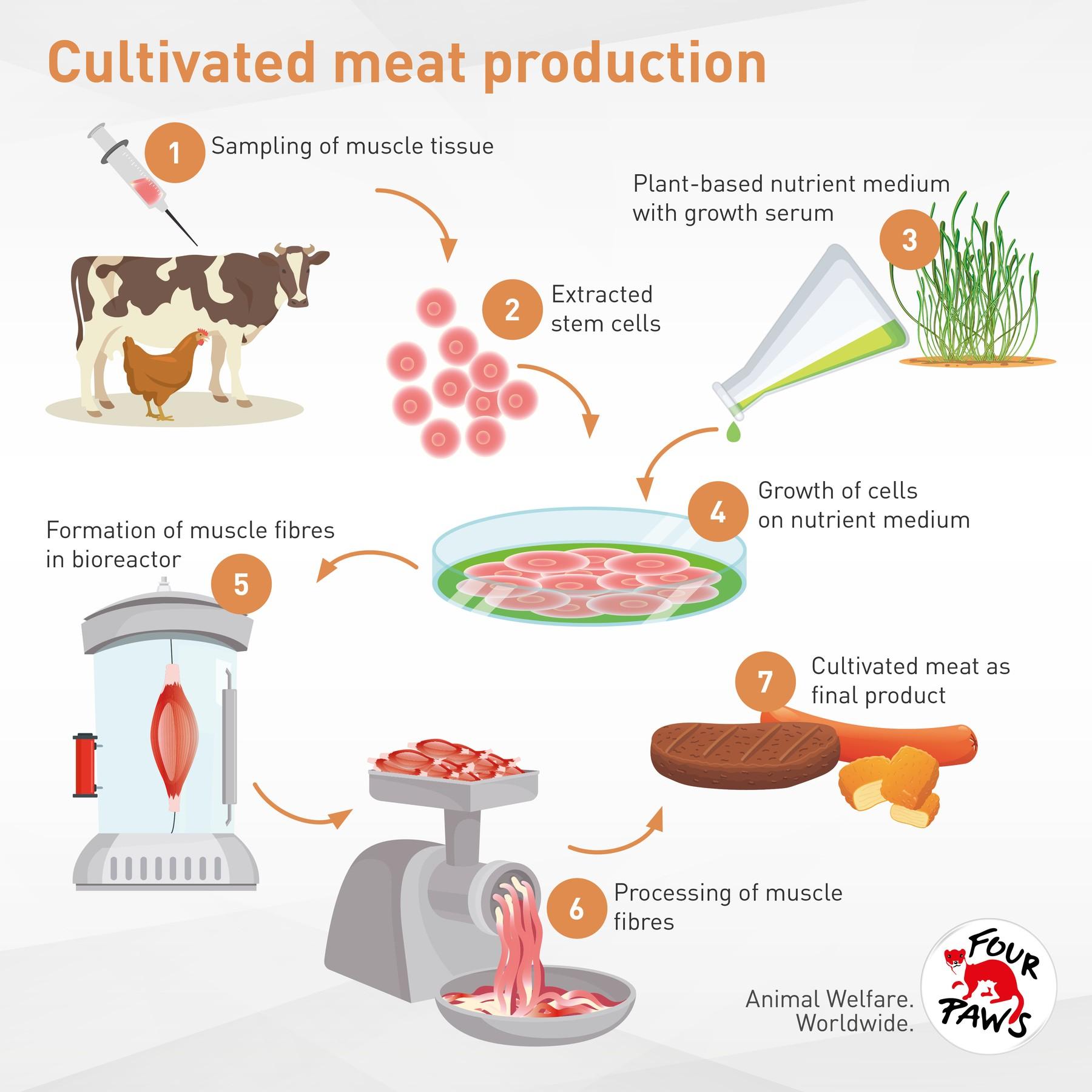
While the promise of lab-grown meat tantalizes with a future of ethical and sustainable food production, the industry faces a significant challenge: scaling up production to meet potential consumer demand. This hurdle represents a complex interplay of scientific, technological, and economic factors that need to be addressed for cultivated meat to truly make its mark.
The Current State of Play: From Labs to Limited Plates
The year 2023 marked a turning point for cultivated meat with the historic approval by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) for two companies to sell cultivated chicken to consumers. This regulatory green light signaled a shift from purely research-oriented endeavors toward commercialization.
However, the current production capacity of cultivated meat remains a far cry from conventional meat production. Most companies are operating pilot plants capable of producing a few kilograms of cultivated meat at a time, a minuscule amount compared to the millions of tons of traditional meat consumed annually.
The Bottlenecks: A Closer Look at the Challenges
Several key bottlenecks are hindering the mass production of cultivated meat:
1. Cost of Production
Currently, producing a single pound of cultivated meat can cost hundreds, even thousands, of dollars. This high cost is primarily attributed to the expensive growth media used to feed the cells. This nutrient-rich broth, often containing fetal bovine serum (FBS), is crucial for cell growth but significantly drives up expenses.
Data Point: A 2020 study by the Good Food Institute estimated that the cost of producing cultivated meat could range from $2.57 to $242.81 per kilogram, with the cost of growth media accounting for a substantial portion of the overall expenses.
2. Bioreactor Design and Optimization
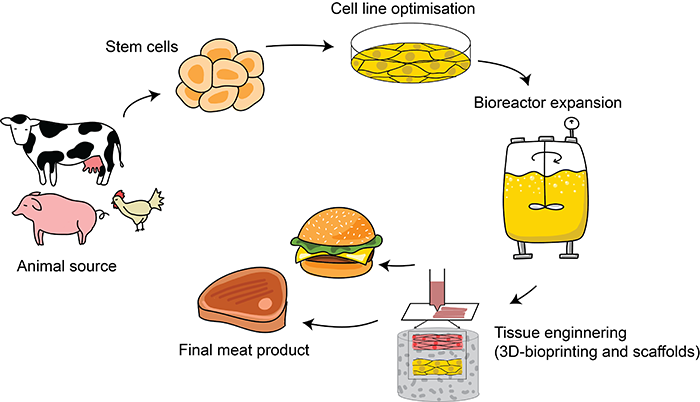
Cultivated meat cells are grown in large stainless-steel vessels called bioreactors. Scaling up production necessitates larger and more efficient bioreactors, pushing the boundaries of existing bioreactor technology. Current designs often face challenges in maintaining optimal conditions for cell growth at larger volumes, impacting both efficiency and scalability.
3. Cell Line Development
Developing robust cell lines capable of proliferating rapidly and efficiently is paramount for large-scale production. Research is ongoing to identify and optimize cell lines that exhibit high growth rates, require fewer nutrients, and can be cultivated for longer durations, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing costs.
Innovations Paving the Way for a Scalable Future
Despite these challenges, the field of cultivated meat is witnessing significant innovations aimed at overcoming these bottlenecks:
1. Plant-Based Growth Media
Researchers are actively developing plant-based alternatives to FBS and other expensive growth media components. These alternatives, often derived from sources like yeast, fungi, and algae, promise to significantly reduce production costs and improve the sustainability profile of cultivated meat.
2. Bioreactor Advancements
Companies are investing heavily in developing novel bioreactor designs specifically tailored for cultivated meat production. These innovations focus on optimizing nutrient delivery, oxygen transfer, and waste removal to support cell growth at larger scales.
3. Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation, a technique used to produce specific ingredients through microbial fermentation, is playing a crucial role in creating key components of cultivated meat, such as heme, the iron-containing molecule responsible for the meaty flavor. This approach offers a more sustainable and cost-effective way to replicate the sensory experience of conventional meat.
Concluding Thoughts: A Future Shaped by Collaboration and Innovation
While significant challenges remain on the path to scaling up cultivated meat production, the industry is buzzing with activity and innovation. Collaboration between scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs, coupled with continued investment in research and development, will be crucial in driving down costs, improving efficiency, and ultimately bringing cultivated meat to the masses.
As research advances and technology matures, we can expect to see significant progress in the scalability of cultivated meat production in the coming years, bringing us closer to a future where this novel food source can contribute to a more sustainable and ethical food system.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dog-treats-glass-storage-container-3f5d7e36-81df4011d844459c9272c9c8404bc38d.jpg)











Comments ()