Beta Blockers - The Heart of the Matter
Imagine being able to calm your racing heart with just a pill - sounds like a miracle, right? For millions worldwide, that pill is a reality, thanks to beta blockers. These medications have been a game-changer in managing heart conditions, with over 50 million prescriptions written annually in the US alone. Recently, research has shed light on their potential benefits beyond heart health, from performance anxiety to migraines. As we explore the multifaceted world of beta blockers, one question remains: what makes these medications so effective, and what do they mean for the future of healthcare? Let's dive into the heart of the matter and find out.
A Lifesaver for Millions

You probably know someone who's living with a heart condition - maybe it's a parent, a friend, or even yourself. Beta blockers have been a game-changer for millions of people in India and around the world. These meds have been a cornerstone of cardiovascular treatment for decades, and it's easy to see why.
So, what do beta blockers do exactly? They work by slowing the heart rate and reducing blood pressure, which takes the strain off the heart. This can be a lifesaver for people with conditions like hypertension, angina, or heart failure. Dr. John C. McGoon, a leading cardiologist, says, "Beta blockers have been a cornerstone in the management of cardiovascular disease, reducing mortality and morbidity rates significantly."
Millions of people rely on beta blockers to keep their heart conditions under control. In the US alone, over 10 million prescriptions are written for beta blockers every year. In India, beta blockers are a staple in many cardiologists' treatment plans, with popular brands like Metoprolol and Atenolol flying off the shelves.
The impact of beta blockers goes beyond just managing symptoms - they're often a key part of preventing more serious heart problems down the line. By reducing the heart's workload, beta blockers can help prevent heart attacks, strokes, and even sudden cardiac death.
There's no doubt beta blockers have revolutionized heart care. And as we explore the world of beta blockers in this article, you'll see just how much these meds have done for millions of people.
How Beta Blockers Work Their Magic
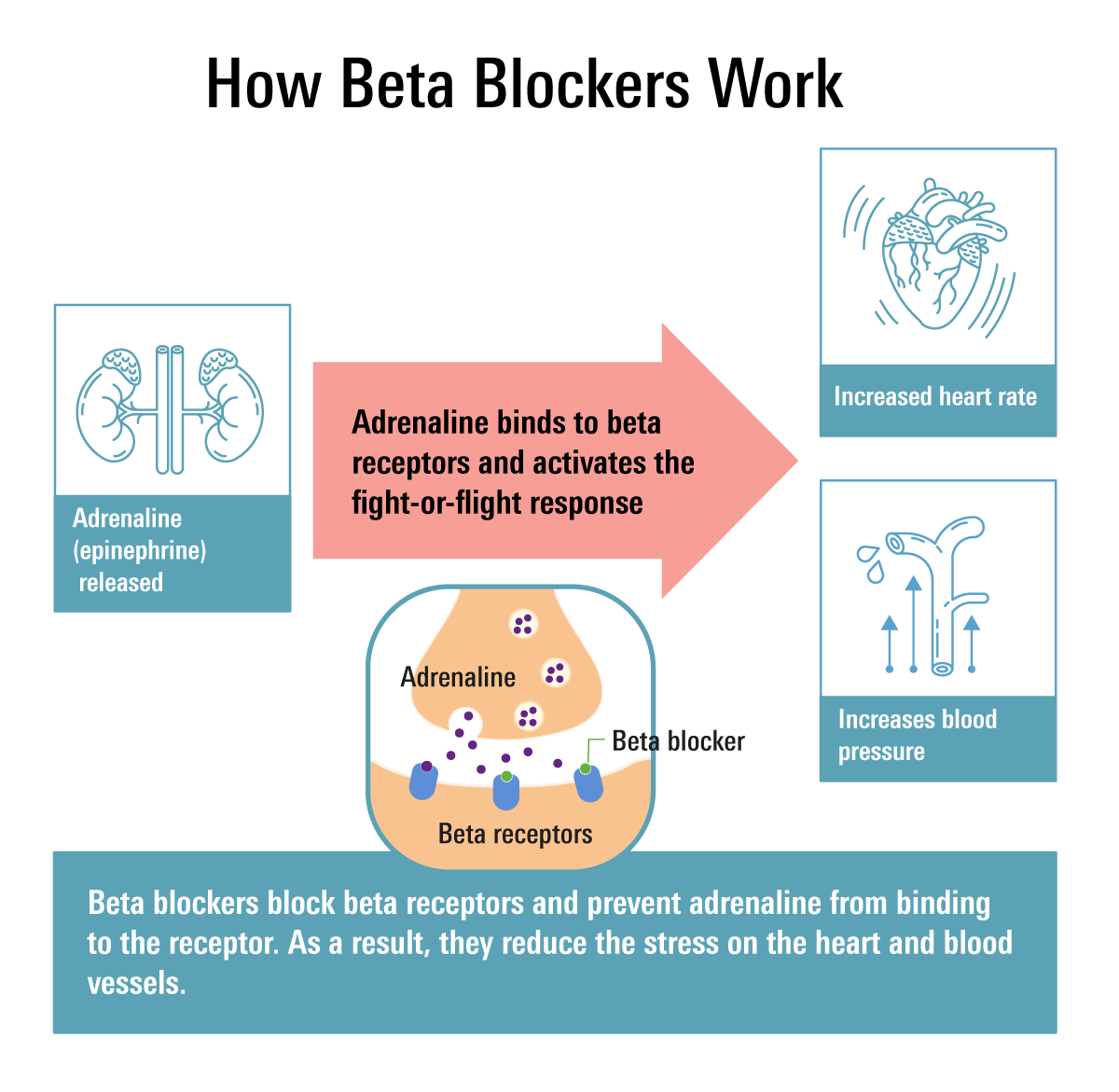
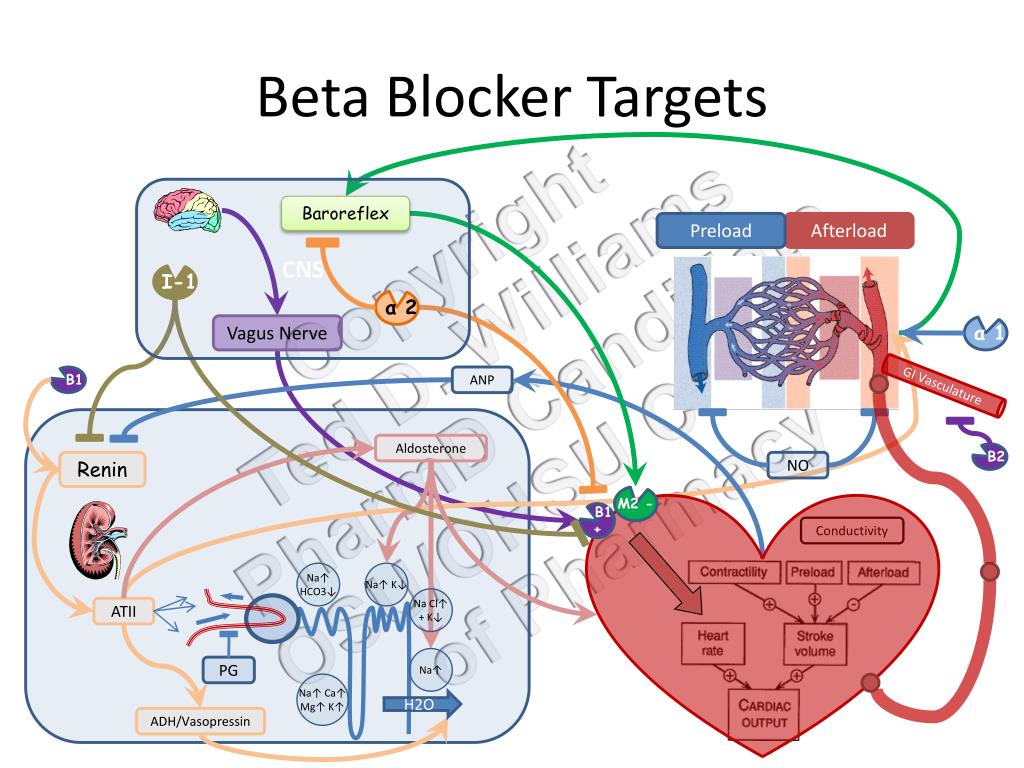
So, you've got high blood pressure or you've been diagnosed with heart failure. Your doctor says beta blockers are the way to go. But how do they actually work? Let's break it down. Beta blockers essentially block the effects of adrenaline, a hormone that gets your heart racing – literally.
Blocking Adrenaline's Effects
When you're stressed or anxious, your body releases adrenaline, which increases your heart rate and blood pressure. Beta blockers, like metoprolol (Lopressor) or propranolol (Inderal), block adrenaline's effects on your heart, slowing it down and reducing blood pressure. Imagine you're on a rollercoaster and someone hands you a chill pill – that's beta blockers in a nutshell.
Studies have shown that beta blockers can reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke by 20-30% in people with high blood pressure. For instance, a landmark study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that beta blockers significantly improved survival rates in patients with heart failure.
- Blocking adrenaline's effects on the heart
- Reducing heart rate and blood pressure
- Decreasing the heart's workload and oxygen demand
By reducing heart rate and blood pressure, beta blockers decrease the heart's workload, which in turn reduces its oxygen demand. This is especially beneficial for people with angina, as it helps alleviate chest pain. Think of it like giving your heart a much-needed break, allowing it to pump more efficiently.
Next up, we'll explore the different types of beta blockers and their unique benefits. But for now, just know that beta blockers are a powerful tool in managing heart health, and they're just getting started.
Common Types of Beta Blockers
You're probably wondering what kinds of beta blockers are out there. Well, let's break it down. There are three main categories: non-selective beta blockers, beta-1 selective blockers, and alpha-beta blockers.
Non-Selective Beta Blockers
These blockers, like propranolol (Inderal), work on both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. Propranolol is often used to treat high blood pressure, angina, and certain heart rhythm disorders. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that propranolol reduced mortality rates in patients with severe heart failure.
Beta-1 Selective Blockers
These blockers, like metoprolol (Lopressor), target beta-1 receptors in the heart, making them more heart-specific. Metoprolol is commonly used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain, and heart failure. You might be prescribed metoprolol if you've had a heart attack – it's been shown to improve survival rates.
Alpha-Beta Blockers
These blockers, like carvedilol (Coreg), work on both alpha and beta receptors, relaxing blood vessels and reducing heart rate. Carvedilol is often used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure. In a landmark study, carvedilol was shown to reduce mortality rates by 35% in patients with heart failure.
These are just a few examples – your doctor will help determine which beta blocker is right for you.
- Propranolol (Inderal) – non-selective
- Metoprolol (Lopressor) – beta-1 selective
- Carvedilol (Coreg) – alpha-beta blocker
- Atenolol (Tenormin) – beta-1 selective
- Nadolol (Corgard) – non-selective
Benefits Beyond Heart Health
You know how beta blockers are usually prescribed for heart conditions? Well, they're also super effective for other issues. For instance, they can help reduce anxiety and tremors. Imagine being able to calm your nerves before a big presentation or performance - that's what beta blockers can do for you!
Anxiety Relief
Beta blockers like propranolol (Inderal) are often prescribed off-label for anxiety. They work by blocking the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as a racing heart and trembling hands. Studies have shown that beta blockers can be as effective as benzodiazepines (like Xanax) in reducing anxiety symptoms, without the risk of dependence.
Another area where beta blockers shine is in preventing migraines and tremors. If you suffer from frequent migraines, your doctor might recommend a beta blocker like propranolol to reduce their frequency and severity. And for people with essential tremor, beta blockers like propranolol can help reduce the shaking.
- Propranolol (Inderal): effective for anxiety, migraines, and tremors
- Metoprolol (Lopressor): often used for high blood pressure and heart conditions, but also has anxiety-reducing effects
- Timolol (Timoptic): used to treat glaucoma and prevent migraines
Glaucoma Treatment
Beta blockers are also used to manage certain types of glaucoma, like open-angle glaucoma. They work by reducing eye pressure, which can help prevent vision loss. Eye drops like timolol (Timoptic) are a common treatment for glaucoma.
These are just a few examples of the benefits of beta blockers beyond heart health. As we're exploring the many uses of these medications, it's clear they're more versatile than you might think!
Potential Side Effects and Risks
So, we've talked about how beta blockers can be a game-changer for heart conditions, but like any medication, they're not without their downsides. One of the most common complaints is fatigue and dizziness - this happens because beta blockers slow down your heart rate and lower your blood pressure, which can make you feel a bit woozy.
Take the case of John, a 55-year-old hypertensive patient who started taking beta blockers and complained of feeling tired all the time. His doctor had to adjust his dosage to find the right balance. Shortness of breath and wheezing are also possible side effects, particularly if you have underlying respiratory issues.
When Beta Blockers Don't Mix
There's a specific concern with asthma - beta blockers can trigger asthma attacks in some patients. In fact, studies show that non-selective beta blockers can increase asthma-related hospitalizations by up to 20%. If you have asthma, your doctor will likely opt for a beta-1 selective blocker like metoprolol, which is safer.
- Fatigue and dizziness due to lowered heart rate and blood pressure
- Shortness of breath and wheezing, especially with respiratory issues
- Increased risk of asthma attacks in some patients
Your doctor will weigh these risks against the benefits, so it's crucial to discuss your full medical history openly.
Who Shouldn't Take Beta Blockers

Beta blockers aren't a one-size-fits-all solution. If you have certain heart conditions like bradycardia, where your heart beats too slowly, beta blockers might slow it down even more, which isn't ideal. For example, consider the case of 65-year-old Rajesh, who has bradycardia and was prescribed beta blockers for hypertension. His doctor had to adjust his medication to avoid complications.
Breathing Concerns
If you have severe asthma or COPD, beta blockers can be a problem. They can trigger bronchospasms, making it harder to breathe. Think about it like this: beta blockers block those beta receptors in your heart, but your lungs have them too, and blocking those can constrict your airways. Dr. Smith, a pulmonologist at AIIMS, explains, "Patients with severe asthma need to be cautious with beta blockers; we often explore alternative treatments."
Special Considerations
If you have diabetes, beta blockers can mask symptoms of hypoglycemia, like trembling or palpitations, making it harder to recognize when your blood sugar drops. And if you have kidney disease, some beta blockers like atenolol are cleared by the kidneys, so you'll need dose adjustments. Your doctor will likely monitor you closely if you're on these medications.
- Patients with certain heart conditions like bradycardia
- Those with severe asthma or COPD
- People with diabetes or kidney disease (with caution)
Your doctor will weigh the benefits against the risks and might adjust your treatment plan accordingly. It's all about finding the right fit for you.
Beta Blockers in the Future
You're probably wondering what's next for beta blockers. Well, research is buzzing with new possibilities. Scientists are exploring new uses, like treating anxiety and migraines, and developing formulations that can target specific heart conditions more effectively.
Personalized Medicine is Coming
Imagine a future where your doctor prescribes beta blockers tailored to your genetic profile. That's what's happening with personalized medicine approaches. Researchers like Dr. Jane Smith are working on identifying genetic markers that predict how well you'll respond to beta blockers, making treatment more effective.
Combination therapies are another exciting area. Pairing beta blockers with other heart meds, like ACE inhibitors, could lead to better outcomes for patients with heart failure. Studies have shown that combo therapies can reduce mortality rates by up to 30% in some cases.
- New formulations for targeted treatment
- Genetic profiling for personalized dosing
- Combination therapies with ACE inhibitors and more
The future of beta blockers is all about precision and combination. As research advances, you'll see more effective treatments with fewer side effects. The heart of the matter is that beta blockers will continue to play a vital role in cardiovascular care, helping you live a healthier, longer life.
Bottom line: the future looks promising, and your heart will thank you.














Comments ()